What is Design thinking?
Verified
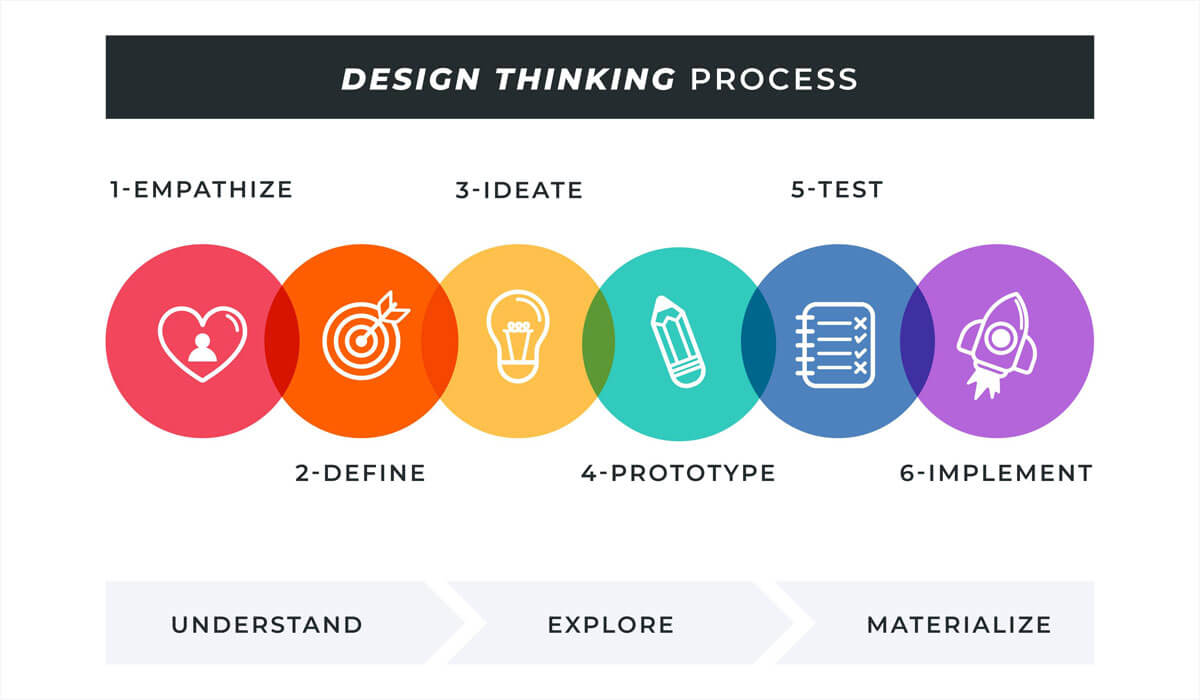
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that is
focused on understanding users' needs and creating innovative solutions to meet
those needs. It is a human-centered approach that emphasizes empathy,
collaboration, experimentation, and iteration.
The design thinking process typically consists of five
stages:
Empathize: In
this stage, designers seek to understand the needs and behaviors of users
through observation, interviews, and other research methods.
Define: Based on
the insights gathered in the empathy stage, designers define the problem they
are trying to solve and the goals they want to achieve.
Ideate: In this
stage, designers brainstorm and generate a wide range of ideas for solving the
problem, without worrying about feasibility or practicality.
Prototype:
Designers create low-fidelity prototypes of their ideas, such as sketches or
mockups, to test and refine their concepts.
Test: In this
stage, designers test their prototypes with real users to gather feedback and
insights, which they use to refine and improve their designs.
The design thinking approach is widely used in various
fields, including product design, service design, and social innovation, and is
seen as a valuable tool for fostering creativity, innovation, and user-centered
design.
What is the
purpose of design thinking?
The purpose of design thinking is to solve complex problems
in a human-centered and innovative way. It is a problem-solving approach that
emphasizes understanding users' needs, generating creative ideas, and testing
and refining solutions through iteration.
Design thinking is used to create products, services, and
experiences that are more effective, efficient, and satisfying for users. It
helps designers and innovators to approach problems from a user's perspective,
rather than focusing solely on technical or business requirements.
Design thinking is also used to foster collaboration and
creativity within teams. It encourages a culture of experimentation and
iteration, where failure is seen as an opportunity for learning and
improvement.
Overall, the purpose of design thinking is to create better
solutions to complex problems, and to do so in a way that is more
user-centered, collaborative, and innovative. By using this approach, designers
and innovators can create solutions that better meet the needs of users, and
are more likely to be successful in the marketplace.
What is the
key of design thinking?
The key to design thinking is a human-centered approach,
which means putting the needs and experiences of users at the forefront of the
problem-solving process. Here are some of the key principles of design
thinking:
Empathy:
Understanding the needs and experiences of users through observation,
interviews, and other research methods.
Collaboration:
Working in interdisciplinary teams to bring together different perspectives and
expertise.
Ideation:
Generating a wide range of ideas, without worrying about feasibility or
practicality.
Prototyping:
Creating low-fidelity prototypes to test and refine ideas.
Iteration:
Testing and refining solutions through multiple iterations, based on feedback
and insights gathered from users.
Experimentation:
Trying new ideas and approaches, and being open to failure as an opportunity
for learning and improvement.
By following these principles, designers and innovators can create
solutions that are more user-centered, creative, and effective. The key to
design thinking is to approach problems from a human-centered perspective, and
to use collaboration, creativity, and experimentation to create better
solutions.
How is
design thinking used in real life?
Design thinking is used in various industries and domains to
solve complex problems, create innovative products and services, and improve
the user experience. Here are some real-life examples of how design thinking is
used:
Product design:
Companies like Apple and IDEO use design thinking to create products that are
user-friendly, aesthetically pleasing, and innovative. For example, the iPod
was designed with a user-centered approach, where designers focused on making
it easy for users to find and play their music.
Service design:
Design thinking is also used to create better services that meet users' needs
and expectations. For example, healthcare organizations use design thinking to
improve patient experiences, such as creating more comfortable waiting areas or
simplifying the check-in process.
Social innovation:
Design thinking can also be used to address social and environmental issues,
such as poverty or climate change. For example, the design thinking approach
has been used to create low-cost, sustainable housing solutions for people in
developing countries.
Education: Design
thinking is increasingly being used in education to foster creativity,
innovation, and problem-solving skills among students. Teachers and educational
institutions use design thinking to create more engaging and effective learning
experiences.
Government:
Design thinking is used in the public sector to improve the delivery of
government services, such as streamlining the process for applying for permits
or creating more accessible transportation systems.
Overall, design thinking is a versatile and powerful
approach that can be applied to various contexts and domains to solve complex
problems and create better solutions.
Why Is It
So Popular?
The popularity of design thinking can be attributed to
several factors.
First, design thinking provides a structured and systematic
approach to problem-solving, which can be applied to a wide range of contexts
and challenges. It offers a way to approach complex problems in a more
innovative and user-centered way, which can lead to more effective solutions.
Second, design thinking is highly adaptable and can be used
in different industries and domains. It can be applied to product design,
service design, social innovation, and education, among others.
Third, design thinking fosters collaboration and teamwork,
bringing together individuals with different backgrounds and expertise to work
towards a common goal.
Finally, design thinking encourages experimentation and
iteration, which means that failure is seen as an opportunity for learning and
improvement. This can lead to more innovative and successful outcomes in the
long run.
Overall, design thinking has gained popularity because it
provides a structured and human-centered approach to problem-solving that can
be applied to various contexts and domains, and fosters collaboration,
creativity, and experimentation.
What is an
example of design thinking?
Here's an example of how design thinking can be applied:
Let's say a company wants to create a new mobile app that
helps people manage their daily tasks more effectively. The company would start
the design thinking process by:
Empathizing: They
would conduct user research, such as interviews or surveys, to understand
users' needs, behaviors, and pain points when it comes to managing tasks.
Define: Based on
the insights gathered in the empathy stage, the company would define the
problem they are trying to solve and the goals they want to achieve. For
example, the company may define the problem as "Users struggle to manage
their tasks effectively, leading to stress and frustration."
Ideate: The
company would brainstorm and generate a wide range of ideas for solving the
problem. For example, they may come up with ideas like using gamification
techniques to make task management more engaging, or incorporating social
features to encourage collaboration and accountability.
Prototype: The company
would create low-fidelity prototypes of their ideas, such as wireframes or
mockups, to test and refine their concepts. They may create several versions of
the app with different features or designs.
Test: The company
would test their prototypes with real users to gather feedback and insights,
which they would use to refine and improve their designs. They may conduct user
testing sessions, or release a beta version of the app to a small group of
users for feedback.





_(1).png)